Economic Growth:
Africa has experienced significant economic growth over the past two decades, with an average annual GDP growth rate of around 3-5%. Several African countries have consistently ranked among the fastest-growing economies in the world. The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), launched in January 2021, aims to create a single market for goods and services across the continent, boosting intra-African trade and creating new business opportunities.

Market Size and Consumer Potential:
Africa has a population of over 1.3 billion people, making it the second-most populous continent. By 2050, Africa’s population is projected to reach 2.5 billion, offering a vast consumer market. Africa’s middle class is expanding rapidly, creating a growing consumer base with increasing purchasing power and demand for goods and services.

Natural Resources and Extractive Industries:
Africa is rich in natural resources, including minerals, oil, gas, and agricultural products. It possesses approximately 30% of the world’s mineral reserves.
The extractive industries sector presents investment opportunities for companies involved in mining, oil exploration, refining, and related infrastructure development.

Infrastructure Development:
Africa requires substantial infrastructure development to support its growing population and economic activities. This includes transportation, energy, telecommunications, and urban development. There is a need for private sector involvement in infrastructure projects, offering opportunities for construction, engineering, renewable energy, and technology companies.

Technology and Digital Economy:
The digital economy in Africa is rapidly expanding, driven by increased mobile phone penetration, growing internet access, and a young, tech-savvy population. E-commerce, fintech, mobile banking, and digital services sectors are witnessing significant growth and present lucrative opportunities for investment and innovation. Africa is experiencing a digital revolution, with innovative solutions emerging to address various challenges and gaps in the market. Businesses, particularly those in the technology sector, can contribute by developing and providing solutions tailored to the African context, such as mobile banking, e-commerce platforms, agri-tech solutions, and telemedicine.

Agriculture and Agribusiness:
Africa has vast agricultural potential due to its fertile land, favorable climate, and water resources. However, the sector requires modernization, investment in agribusiness, and value chain development. Agribusiness opportunities include food processing, storage and logistics, agricultural equipment and technology, and export of agricultural products.

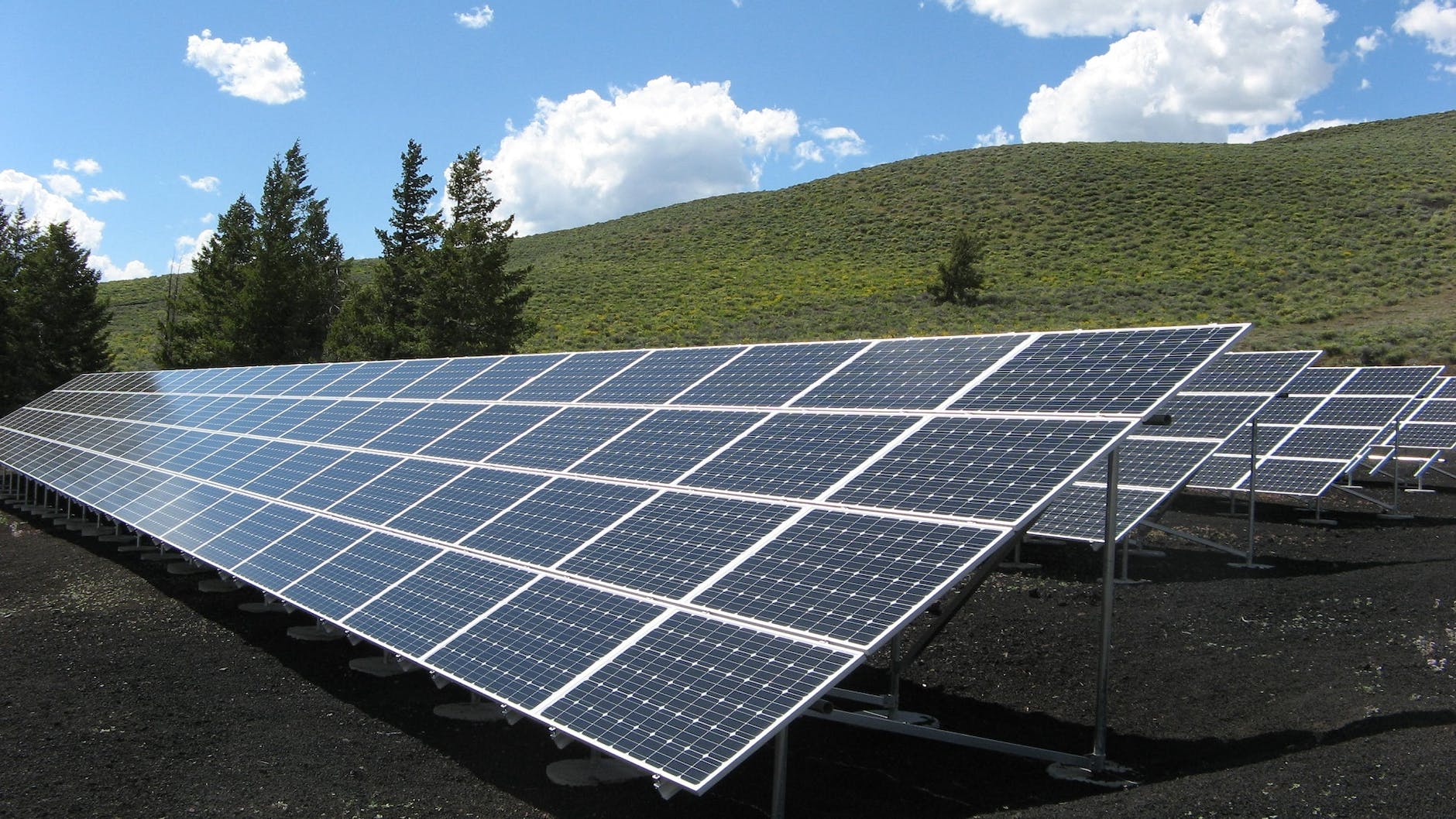
Renewable Energy:
Africa has abundant renewable energy resources, including solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal. The continent is making strides in renewable energy development to meet growing energy demands and address climate change. There is a need for private sector participation in renewable energy projects, including power generation, distribution, and energy efficiency solutions.

Youthful Workforce:
Africa has the youngest population globally, with a significant proportion under the age of 25. This youthful workforce offers a demographic dividend and a potential labor pool for businesses to tap into.

Government Initiatives:
Many African governments are implementing economic reforms, improving the business environment, and promoting foreign direct investment (FDI) through incentives, tax breaks, and regulatory reforms.

Regional Integration and Trade Partnerships:
African countries are actively engaging in regional integration efforts, promoting trade agreements, and strengthening economic ties within the continent and with international partners. The AfCFTA is expected to create a unified African market and boost trade by eliminating trade barriers, fostering cross-border investments, and facilitating business expansion.

Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
Businesses and social impact organizations can align their activities with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to address these challenges while creating economic opportunities.

Job Creation and Economic Empowerment:
Africa’s regulatory, private sector and civil society frameworks are geared towards initiatives that support entrepreneurship, skills development, and microfinance, empowering individuals and communities to participate in the economy.

Social Infrastructure and Services:
Businesses and organizations can play a crucial role in improving social infrastructure and services in Africa, such as healthcare, education, and access to clean water and sanitation. Investing in healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and sustainable infrastructure projects not only improves quality of life but also strengthens the overall social fabric of communities.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs):
Collaboration between the public sector, private businesses, and social impact organizations through PPPs can drive sustainable development in Africa. PPPs can leverage the strengths and resources of each sector to address complex challenges, such as infrastructure development, healthcare provision, and education initiatives.

Access to Essential Services:
Many underserved communities in Africa lack access to essential services, such as electricity, clean water, and financial services. Businesses and social impact organizations can develop innovative models to provide affordable and accessible solutions, such as off-grid renewable energy solutions, water purification systems, and mobile banking services.

Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Businesses operating in Africa can integrate social and environmental considerations into their operations through CSR initiatives. CSR programs can focus on community development, environmental conservation, skills training, and supporting local entrepreneurs, fostering sustainable economic growth while positively impacting local communities.

Inclusive Business Models:
Inclusive business models aim to create shared value by addressing social or environmental challenges while generating profits. By designing products and services that are affordable, accessible, and tailored to the needs of underserved populations, businesses can expand their customer base and make a positive impact on people’s lives.

Overall, Africa presents a fertile ground for businesses, the public sector, and social impact organizations to contribute to economic growth while simultaneously making a tangible and lasting impact on the lives of individuals and communities across the continent. By adopting sustainable and socially responsible practices, organizations can drive positive change and create shared value for both shareholders and society.